Types, Formation, Global Reserves, and Industrial Applications
What Is Barite?
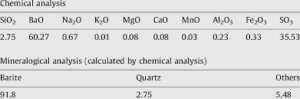
Barite (also known as baryte) is a mineral composed of barium sulfate (BaSO₄). It is a heavy, white to light-colored mineral naturally occurring in the earth’s crust. The name “barite” comes from the Greek word barus, meaning heavy, which reflects its high density—one of its most defining characteristics.
Although barite is primarily used in the oil and gas industry, it also has diverse applications in medical imaging, paints, coatings, construction, and water treatment. Thanks to its high specific gravity, chemical stability, and non-toxicity, barite plays an essential role in many industrial sectors. As a high-density material, it is especially valuable in drilling fluids for oil and gas operations, as well as in pharmaceutical imaging agents.Barite article
 Types of Barite
Types of Barite
Barite is classified according to its purity, color, and composition, which vary depending on the region where it forms. The main types include:
-
White Barite
-
Purity: High, with very low iron content.
-
Uses: Pharmaceuticals, medical imaging, paints, coatings, and cosmetics.
-
Properties: Chemically inert, which makes it ideal for non-reactive environments.
-
-
Grey Barite
-
Purity: Contains moderate iron and other impurities.
-
Uses: Primarily in oil and gas drilling fluids.
-
Properties: Lower brightness than white barite but still industrially valuable.
-
-
Brown Barite
-
Purity: Similar to grey but with higher iron concentration.
-
Uses: Drilling mud, concrete, and other heavy aggregates.
-
Properties: Brown to reddish-brown hues, depending on iron levels.
-
-
Blue and Purple Barite
-
Purity: Rare; includes trace manganese.
-
Uses: Ornamental or specialized jewelry.
-
Properties: High aesthetic value, appealing to collectors.
-
-
Rose Barite
-
Purity: Contains manganese and trace elements.
-
Uses: Decorative applications.
-
Properties: Distinctive color and mineral makeup.
-
How Barite Forms in Nature
Barite generally forms in sedimentary environments where specific conditions trigger the precipitation of barium sulfate. Several geological processes contribute to its creation:
-
Hydrothermal Deposits
Hot water veins associated with metal sulfide deposits can produce barite. In volcanic regions, geothermal fluids carry barium to cooler zones, where it precipitates as barite crystals. -
Marine Evaporites
In shallow marine basins, evaporation concentrates barium-rich seawater. Eventually, barium sulfate precipitates, creating large sedimentary deposits. -
Residual Deposits
Barite may form in limestone and sandstone beds when rocks undergo alteration. Fault zones often host barite because hydrothermal fluids deposit it within fractures. -
Vein Deposits
Moving fluids within rock fractures deposit barium sulfate, producing barite veins.
Barite Reserves Around the World
Barite occurs worldwide, yet some nations dominate both production and export.
-
China – World’s Leading Producer
China accounts for nearly 40% of global production, with major reserves in Guizhou, Hunan, and Guangxi. These deposits supply drilling, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic markets. China consistently leads global exports. -
India
India ranks second, producing barite in Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan. It serves the Middle East and Southeast Asia through significant exports. -
United States
Major reserves in Nevada, Georgia, and Missouri meet much of the domestic oil and gas sector’s needs. However, the U.S. also imports barite, mainly from China and Mexico. -
Morocco
Morocco’s high-purity deposits, especially in Sidi Lahcen, supply North America and Europe.Barite article -
Mexico
Reserves in Baja California and Sonora focus on oil and gas drilling demand, often exported to the U.S. -
Other Producers
Turkey, Iran, Russia, Pakistan, Peru, and Brazil also maintain growing production and market presence.
Regional Production Overview
-
Asia-Pacific: China dominates, while India remains a strong second, serving Asia and the Middle East.
-
North America: The U.S. meets part of its needs domestically, but Mexico is a crucial supplier.
-
Europe: Morocco and Turkey are key exporters to the EU market.
-
Middle East & Africa: Iran is increasing production, and Morocco remains a major global player.
-
Latin America: Brazil and Peru continue to expand their influence in regional and global trade.Barite article
Industrial Applications of Barite
-
Oil and Gas Industry
Barite increases drilling fluid density to control pressure, prevent blowouts, and stabilize wellbores. It also helps cool drilling equipment and suspend cuttings. -
Paints, Coatings, and Plastics
As a filler and pigment, barite improves opacity, brightness, UV resistance, and durability. -
Medical and Pharmaceutical Industry
Barite serves as a contrast agent in X-rays and CT scans. It also aids in radiation shielding in hospitals and nuclear facilities. -
Construction and Building Materials
Heavyweight aggregates from barite strengthen concrete and enhance stability. It also appears in soundproofing and insulation products. -
Water Treatment and Environmental Uses
Barite removes contaminants from drinking water and absorbs hazardous substances during industrial waste treatment.